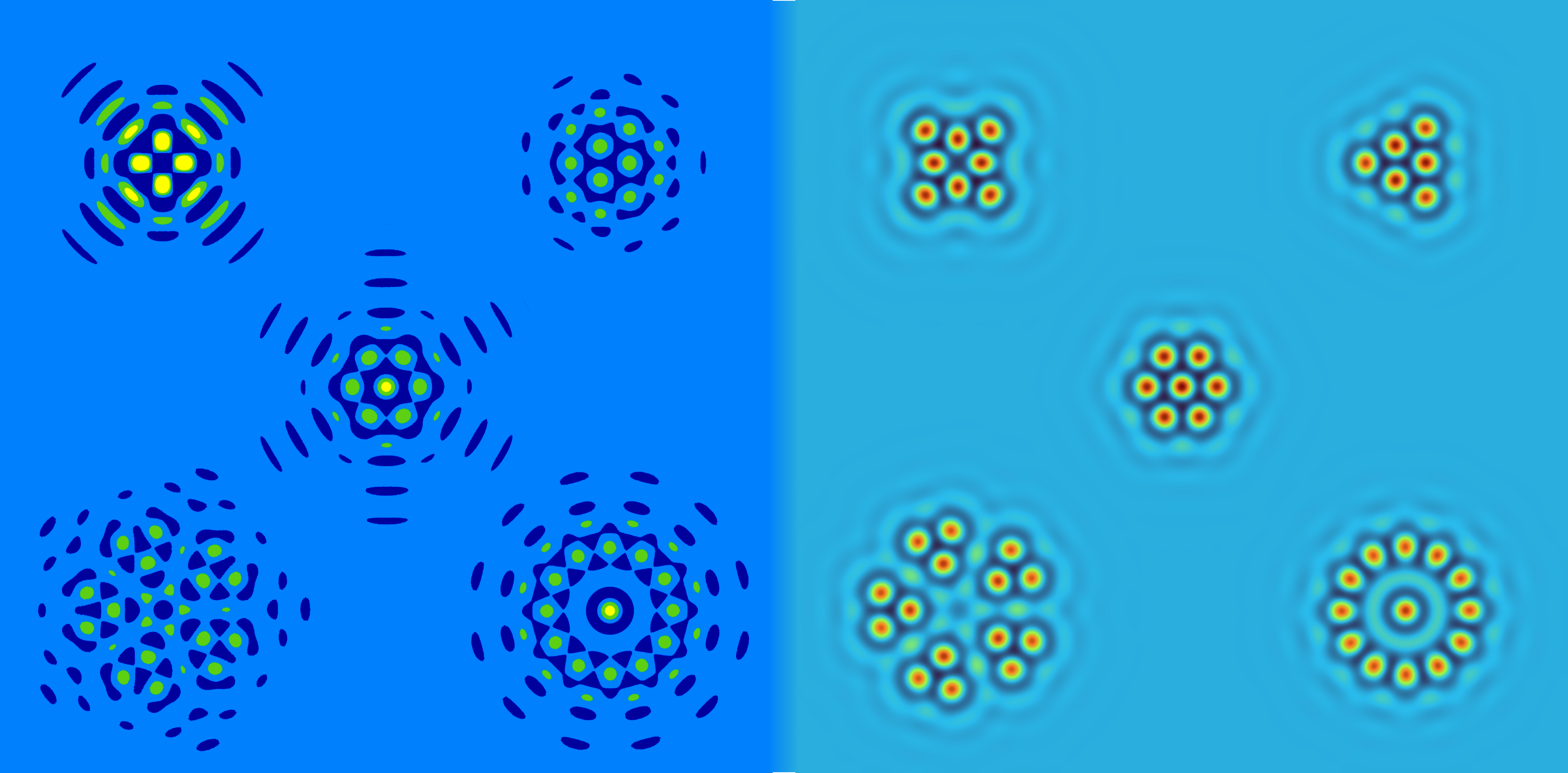
The Swift--Hohenberg equation is a prototypical pattern-forming scalar partial differential equation that is known to exhibit a wide variety of localised structures. In its quadratic-cubic form it is given by
| |
\( \partial_t u = -(1 + \Delta )^2 u - \mu u + \nu u^2 - u^3, \) |
(1) |
where \(\Delta = \partial_x^2 + \partial_y^2\) is the Laplacian operator in Cartesian coordinates \((x,y) \in \mathbb{R}^2\), \(\mu \in \mathbb{R}\) is a bifurcation parameter and \(\nu\) is a parameter that affects the size of the bistability region between the trivial state and the domain-covering hexagon pattern state. While this nonlinear equation has been known to support localised patterns with radial and hexagonal symmetry, recent work in [1] has provided evidence for the existence of patterns exhibiting any dihedral symmetry. This figure uses the approximate solutions from [1] as initial conditions (left) to converge to localised solutions of the Swift--Hohenberg equation (right) using the freely-available VisualPDE software [2]. The converged patterns exhibit 4-fold (top left), 3-fold (top right), 6-fold (middle), 5-fold (bottom left), and 12-fold (bottom right) symmetries.
References
[1] D. J. Hill, J. J. Bramburger, and D. J. Lloyd, Approximate localised dihedral patterns near a Turing instability, Nonlinearity, 36 (2023), p. 2567.
[2] B. J. Walker, A. K. Townsend, A. K. Chudasama, and A. L. Krause, Visualpde: rapid interactive simulations of partial differential equations, Bulletin of Mathematical Biology, 85 (2023), p. 113.
| Author Institutional Affiliation | Concordia University, Saarland University, University of Surrey |
| Author Email | |