COCO is a MATLAB-based, object-oriented platform for constructing composite continuation problems,
mapping out their solution manifolds, and locating special points on these manifolds. The COCO core
provides general-purpose support for these tasks, making the platform extremely versatile and flexible,
even at run time. COCO-compatible toolboxes exemplify common classes of problems that arise in
dynamical systems theory, including bifurcation analysis and design optimization.
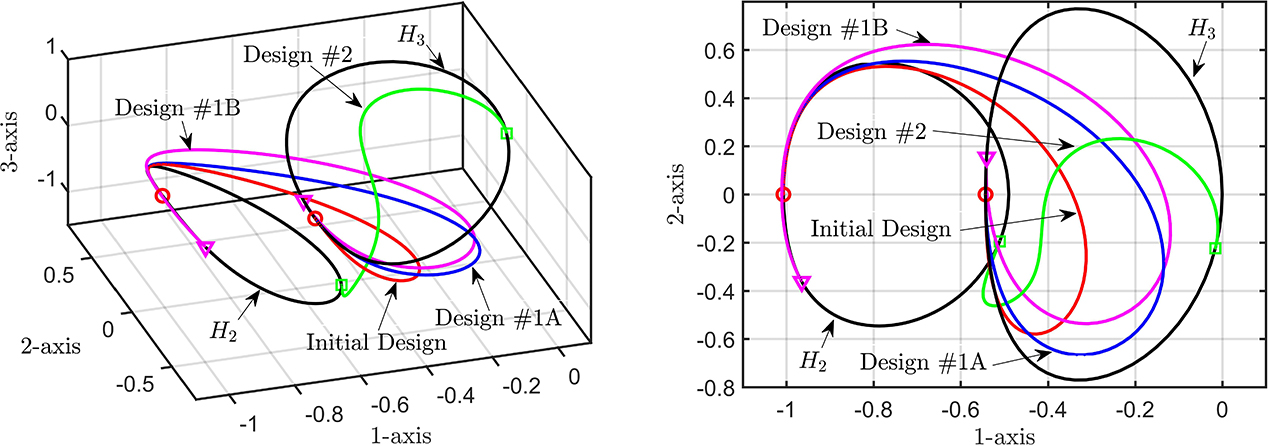
Figure 1. Optimal spacecraft transfer trajectories between halo orbits in the circular, spatial, restricted three-body problem obtained using successive continuation in COCO of solutions to a three-segment multi-point boundary-value problem and the corresponding adjoint equations. This figure was published in SIADS 17-2: https://epubs.siam.org/doi/abs/10.1137/17M1143563.
The package is under ongoing development. Earlier releases (November 2015 and before) were co-developed
by Harry Dankowicz and Frank Schilder (with contributions also by Mike Henderson and Erika Fotsch), while
subsequent development has been developed entirely within Harry's research group. A major new release
was posted to Sourceforge in November 2017. The algorithmic foundation for the new functionality in this release
was documented in a SIADS paper that was accepted for publication in December 2017 and appeared
online in April 2018. This paper was co-authored by Harry Dankowicz and his graduate student Mingwu Li, who also helped with
initial development of code and testing of tutorial demos.
The November 2017 release is available for download at https://sourceforge.net/projects/cocotools/.
Installation instructions are available in the README.txt file that is included with the .zip archive. To run
any demos included with the release, first follow the installation instructions, then change to the
directory where the demo resides, explore the files, and run the demo by entering the demo name on
the command line.
The November 2017 release includes the following new functionality, without precedent in any existing
packages:
- Fully documented support for general-purpose, staged construction of adjoint equations,
consistent with COCO’s object-oriented construction paradigm and the decomposition of
continuation problems into coupled instances of individual continuation objects.
- Full support for adaptive remeshing of adjoint equations, consistent with adaptive updates to
the problem discretization along families of solutions to integro-differential boundary-value
problems.
- Detailed core and toolbox tutorials and demos illustrating a method of successive continuation
for constrained single-objective optimization along
- Solutions to arbitrary algebraic continuation problems;
- Families of equilibrium points in autonomous dynamical systems;
- Families of constrained trajectory segments, e.g., periodic orbits;
- Solutions to composite continuation problems, e.g., coupled periodic orbits.
In this release, the COCO core was augmented to support an expanded definition of COCO-compatible
continuation problems, for example for simultaneous continuation of a zero problem and the associated
adjoint conditions. See help/CORE-Tutorial.pdf for tutorial and reference documentation, including a
fully documented example of single-objective optimization along a family of solutions to an algebraic
continuation problem and related exercises. See the core/examples folder for the corresponding demo.
Furthermore, in this release the existing ep, coll, and po toolboxes were updated to include support for
construction of the associated adjoint equations, as well as demos of constrained design optimization
along families of
- equilibria in smooth, autonomous dynamical systems;
- collections of constrained trajectory segments with independent adaptive discretization in
autonomous or non-autonomous dynamical systems, including single- and multi-segment boundary-value problems; and
- single-segment periodic orbits in smooth, autonomous or non-autonomous dynamical systems,
and multi-segment periodic orbits in hybrid, autonomous dynamical systems.
Extensive tutorial documentation and additional exercises are available in help/EP-Tutorial.pdf,
help/COLL-Tutorial.pdf, and help/PO-Tutorial.pdf with corresponding demos in the ep/examples,
coll/examples, and po/examples folders. A demo in the po/examples folder illustrates constrained
optimization of an integral functional along a family of periodic orbits and demonstrates the ability to
greatly extend the functionality of COCO toolboxes at run time by adhering to the general design
principles and syntax described in the textbook Recipes for Continuation, published by SIAM in 2013.
The code has been tested in Matlab R2016b.
Online documentation shipped already with older releases includes fully commented implementations
of all code printed in Recipes for Continuation, including toolboxes and demos, as well as code used to
generate most of the figures in the book. To explore this content, after installation, enter the command
“doc recipes” on the command line. The code has been tested with Matlab R2015a.
Finally, an introductory suite of video tutorials illustrating the core principles of continuation and their
implementation in COCO is available at http://danko.mechanical.illinois.edu/coco_tutorials.htm. The
video files are also accompanied by a complete transcript.
| Keywords | Bifurcation analysis, numerical continuation |
| Model | |
| Software Type | |
| Language | |
| Platform | |
| Availability | |
| Contact Person | |